CRITICAL CARE
Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation (ECMO)
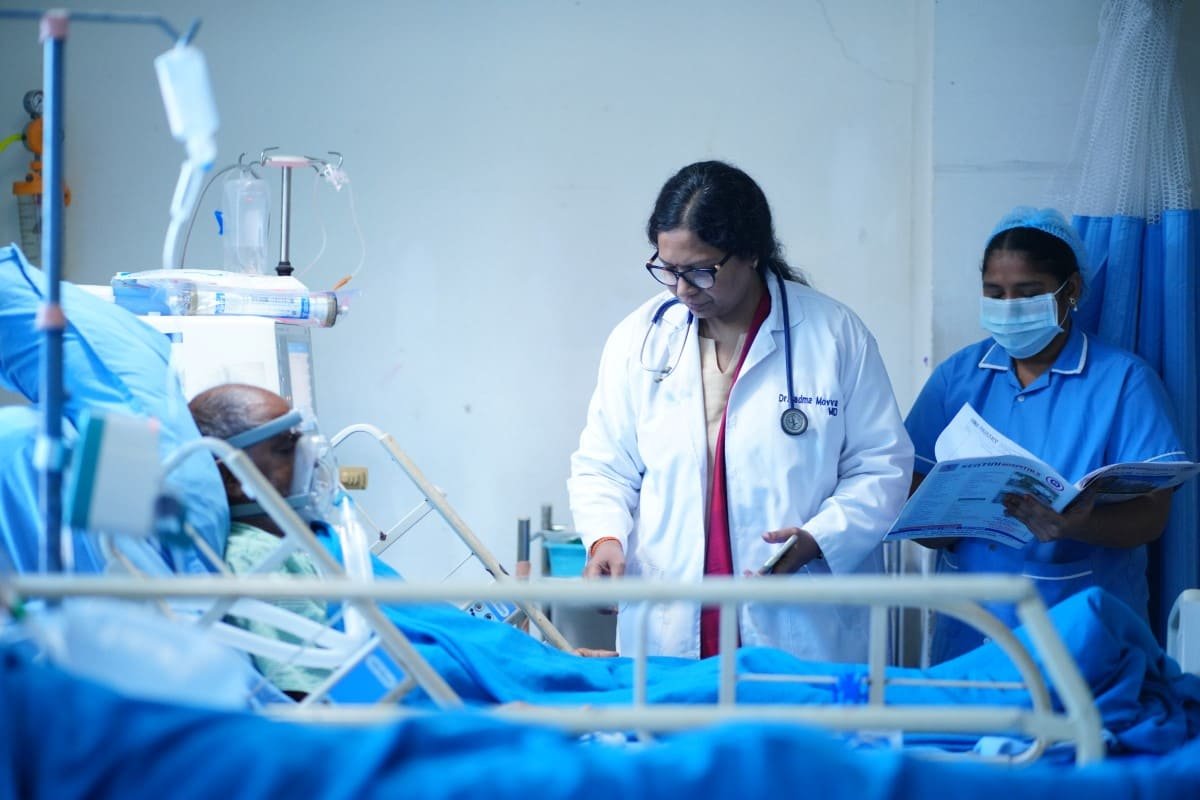
At Sentini Hospitals, we are proud to offer Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation (ECMO) as part of our advanced critical care services. ECMO is a life-saving technology used for patients with severe respiratory or cardiac failure when conventional treatments are insufficient.
What is ECMO?
ECMO is a sophisticated treatment that provides prolonged cardiac and respiratory support by circulating blood outside the body through an artificial lung. This process adds oxygen to the blood and removes carbon dioxide, allowing the heart and lungs to rest and heal.
Key Benefits of ECMO:
- Life-Saving Support: Offers critical support for patients with life-threatening conditions such as severe pneumonia, ARDS, or cardiac arrest.
- Bridge to Recovery: Acts as a temporary measure while awaiting recovery of heart or lung function or as a bridge to further treatment options like a transplant.
- Expert Care: Managed by a dedicated team of Pulmonology and Critical Care specialists, ensuring round-the-clock monitoring and adjustment.
Our ECMO Team:
At Sentini City Hospitals, our ECMO program is led by a team of highly trained specialists in Pulmonology and Critical Care. Our experts work collaboratively to deliver the highest standard of care, using ECMO technology to stabilize patients and improve outcomes in critical situations.
Why Choose Sentini City Hospitals
for ECMO?
- 24/7 Specialist Care: Our ICU is managed 24/7 by a skilled team of Pulmonology and Critical Care specialists, ensuring continuous and expert oversight.
- Advanced Technology: We utilize the latest ECMO technology and protocols to provide cutting-edge care.
- Comprehensive Support: Our multidisciplinary approach ensures that all aspects of the patient’s health are managed, from respiratory function to overall recovery.
Critical care is a specialized medical department that focuses on the treatment of patients with life-threatening illnesses or injuries. This area of healthcare is dedicated to providing intensive and immediate medical attention to individuals who require close monitoring, advanced life support, and specialized interventions. The Critical Care Department, often known as the Intensive Care Unit (ICU), plays a pivotal role in managing critically ill patients, ensuring their stabilization, and facilitating recovery. Here's an in-depth look at the Critical Care Department:
1. Overview of Critical Care:
- Definition: Critical care refers to the specialized medical care provided to patients facing life-threatening conditions, such as severe injuries, trauma, organ failure, or complications following major surgeries.
- Setting: The Critical Care Department is typically housed in hospitals and includes the Intensive Care Unit (ICU), Coronary Care Unit (CCU), and other specialized units.
2. Key Components:
- Multidisciplinary Team: Critical care involves a highly trained and multidisciplinary team, including intensivists, critical care nurses, respiratory therapists, pharmacists, and other specialists.
- Advanced Monitoring: Patients in critical care are closely monitored with advanced equipment to assess vital signs, organ function, and response to treatments in real-time.
- Life Support Systems: Critical care often involves the use of life support systems, including mechanical ventilation, hemodynamic monitoring, and renal replacement therapy.
3. Conditions Treated in Critical Care:
- Trauma: Critical care is essential for managing patients with severe injuries resulting from accidents, falls, or violence.
- Sepsis: The department plays a crucial role in treating patients with systemic infections leading to a life-threatening inflammatory response (sepsis).
- Cardiovascular Emergencies: Conditions like heart attacks, severe heart failure, and life-threatening arrhythmias are managed in the Coronary Care Unit.
4. Procedures and Interventions:
- Mechanical Ventilation: Critical care often involves the use of ventilators to assist or replace a patient's breathing when they are unable to do so adequately.
- Invasive Monitoring: Procedures such as arterial catheterization and central venous catheterization are common for continuous monitoring and administering medications.
- Renal Replacement Therapy: Critical care units are equipped to provide dialysis for patients with acute kidney injury or failure.
5. Importance of Timely Intervention:
- Golden Hour: The concept of the "golden hour" underscores the critical importance of rapid and effective intervention during the initial hour after a patient's injury or onset of a critical illness.
- Decisive Decision-Making: Timely decision-making, often involving rapid diagnostic assessments and interventions, is essential in critical care to improve patient outcomes.
6. Challenges and Innovations:
- Resource Allocation: Critical care often faces challenges related to resource allocation, including the availability of specialized staff, equipment, and space.
- Technological Advances: Ongoing advancements in medical technology, such as telemedicine, precision medicine, and artificial intelligence, are influencing critical care practices.
7. Patient and Family Support:
- Communication: Effective communication with patients' families is a crucial aspect of critical care, providing updates on the patient's condition, prognosis, and involving them in decision-making when appropriate.
- Psychosocial Support: Critical care teams recognize the importance of addressing not only the physical but also the emotional and psychological well-being of patients and their families.
8. Training and Education:
- Specialized Training: Healthcare professionals in critical care undergo specialized training to develop the skills and knowledge required for managing complex and critically ill patients.
- Continuing Education: Given the dynamic nature of critical care, ongoing education and training are essential for staying abreast of new developments and best practices.
In conclusion, the Critical Care Department is a cornerstone of modern healthcare, providing vital support and interventions for patients facing life-threatening conditions. The collaborative efforts of a highly skilled and multidisciplinary team contribute to the overall success of critical care in saving lives and promoting recovery.


.jpg)